How to Create a Lead Distribution System
Routera Team
Content Team
Generating new leads is essential for your business's longevity, as each lead represents a potential customer.
This means new leads should be considered highly valuable and require proper management. After investing significant time and money into lead generation, it's crucial to ensure they're fully fulfilled.
The critical next step after qualifying a lead is connecting it with the appropriate sales representative who can convert it into revenue. This is precisely where an effective lead distribution system becomes a vital component of your sales process.
What Is a Lead Distribution System?
It acts as a bridge between lead generation efforts and the sales process, ensuring that each potential customer receives timely attention from the most suitable representative.
At its core, a lead distribution system is designed to solve several critical challenges:
- Reducing response time to new inquiries
- Ensuring fair allocation of leads among team members
- Matching leads with the most qualified sales representatives
- Preventing leads from falling through the cracks
- Tracking lead progression through the sales funnel
As businesses scale, the volume of incoming leads can become overwhelming, making manual distribution processes inefficient and error-prone. A robust lead distribution system automates this process, allowing sales teams to focus on what they do best: selling.
The Evolution of Lead Distribution Systems
Lead distribution systems has evolved significantly over the years. What once involved manually sorting through business cards and referrals has transformed into sophisticated systems powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms.
Traditional methods of lead distribution often relied on simple round-robin approaches or basic territory assignments. While these methods provided some structure, they lacked the sophistication needed to maximize conversion rates in today's data-driven business environment.
This evolution has transformed lead distribution from a simple administrative function to a strategic advantage that can significantly impact revenue generation.
The Business Impact of Effective Lead Distribution
Key Benefits of Implementing a Lead Distribution System
1. Faster Response Times
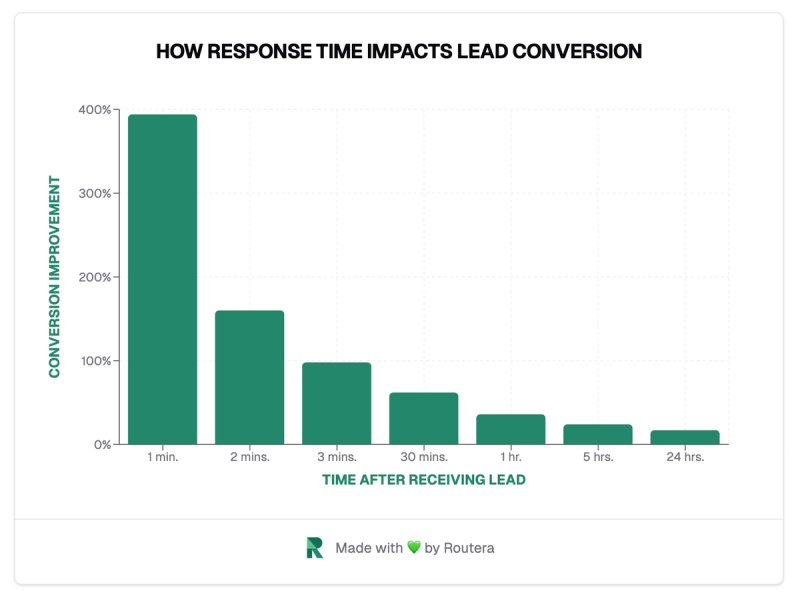
Research consistently shows that the odds of converting a lead decrease dramatically as time passes from the initial inquiry. A well-designed lead distribution system ensures that leads are immediately assigned and acted upon, significantly increasing the likelihood of conversion.
According to industry studies, leads contacted within five minutes of submission are 21 times more likely to enter the sales process compared to those contacted after 30 minutes. This dramatic difference highlights the critical importance of swift lead assignment and follow-up.
2. Improved Lead Matching
Not all sales representatives are equally effective with all types of leads. Some excel at working with enterprise clients, while others may have particular success with specific industries or regions. A sophisticated lead distribution system matches leads with the representatives most likely to convert them based on historical performance data and specific expertise.
This intelligent matching process increases conversion rates while also creating more positive experiences for both sales representatives and potential customers.
3. Balanced Workload Distribution
Uneven lead distribution can lead to various problems within a sales organization. Some representatives may become overwhelmed with too many leads, while others might not receive enough opportunities to meet their targets. This imbalance creates inefficiencies and can contribute to burnout and turnover.
A well-designed lead distribution system ensures equitable allocation of leads based on capacity, expertise, and performance, creating a more balanced and sustainable work environment.
4. Enhanced Data Collection and Analysis
Modern lead distribution systems don't just assign leads; they collect valuable data throughout the process. This information provides insights into:
- Which lead sources produce the highest quality prospects
- Which sales representatives excel with specific types of leads
- How long different types of leads take to convert
- Which stages of the sales process create bottlenecks
These insights allow organizations to continuously refine their lead generation and distribution strategies for optimal results.
5. Increased Revenue and ROI
The cumulative effect of faster response times, better lead-to-representative matching, and data-driven optimization is straightforward: increased revenue and return on investment. Companies that implement effective lead distribution systems typically see significant improvements in conversion rates and sales efficiency.
Building Your Lead Distribution System: A Step-by-Step Approach
Creating an effective lead distribution system requires careful planning and execution. The following steps provide a comprehensive framework for developing a system tailored to your organization's specific needs.
Step 1: Audit Your Current Lead Process
Before implementing a new distribution system, it's essential to understand your current processes, including their strengths and weaknesses.
Conduct a Comprehensive Process Mapping
Document every step from the moment a lead enters your system until it converts to a customer or is disqualified. This mapping should include:
- All lead sources and entry points
- Current assignment methods
- Tracking and follow-up procedures
- Handoff points between teams
- Reporting structures
If you are using HubSpot, a great starting point is create a new contact, or submit a form on your website - then analyze the workflows that the contact is enrolled in.
If you notice the contact owner field is set, you can hover over it and view the details of how the field is set. We use this in auditing specific processes all the time, and I recommend relying on this "Details" option to see how specific values (in this case the owner fields) are being set.
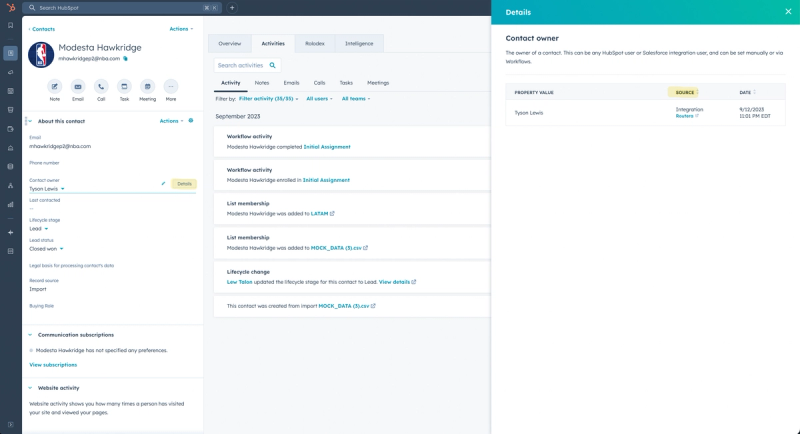
Here is an example in HubSpot how to view the details of how the Contact Owner field was set. In this case they are using Routera as their lead distribution system.
Identify Pain Points and Bottlenecks in Current Lead Distribution Process
Common issues to look for include:
- Delays in lead assignment
- Inconsistent follow-up protocols
- Inadequate lead qualification
- Uneven distribution among team members
- Lack of visibility into lead status
- Poor matching between lead types and sales expertise
Step 2: Define Your Lead Distribution Goals and Requirements
With a clear understanding of your current process, you can establish specific objectives for your new lead distribution system.
Set Quantifiable Goals
Effective goals might include:
- Reducing lead response time from X hours to Y minutes
- Increasing lead-to-opportunity conversion rate by Z%
- Ensuring no representative receives more than X leads per day
- Improving territory coverage by X%
- Reducing lead leakage by X%
Determine Technical Requirements
Consider what functionality your system will need:
- Integration capabilities with your CRM and marketing automation platforms
- Mobile accessibility for field sales teams
- Real-time distribution vs. batch processing
- Automated notifications and alerts
- Reporting and analytics features
- Customizable distribution rules
- Ability to handle peak volumes
Step 3: Choose Your Lead Distribution Model
Several distribution models exist, each with its own advantages and limitations. The right choice depends on your specific business needs and sales structure.
- Round-Robin Distribution
- Skill-Based Routing
- Geographic Distribution
- Capacity-Based Distribution
- Performance-Based Distribution
- Hybrid Models
Round-Robin Distribution
This straightforward approach distributes leads sequentially among team members, ensuring each person receives an equal number of opportunities.
Best for: Teams with similar skills and experience levels where fairness in distribution is a primary concern.
Limitations: Doesn't account for varying expertise or capacity differences among team members.
Skill-Based Routing
This model assigns leads based on sales representatives' specific skills, expertise, or success rates with particular types of leads.
- Best for: Teams with specialized knowledge or varying experience levels where matching expertise to lead characteristics is crucial.
- Limitations: Requires robust data on both lead attributes and sales representative capabilities.
Geographic Distribution
Leads are assigned based on territorial boundaries, ensuring representatives focus on specific regions.
- Best for: Field sales teams or businesses where local knowledge and relationships are important.
- Limitations: Can create imbalances if territories have significantly different lead volumes or quality.
Capacity-Based Distribution
This approach considers each representative's current workload and capacity before assigning new leads.
- Best for: Teams dealing with complex sales cycles where bandwidth for proper follow-up is crucial.
- Limitations: Requires sophisticated tracking of representative workloads and availability.
Performance-Based Distribution
High-performing representatives receive more or higher-quality leads as a reward for their success.
Best for: Creating incentives for top performance and ensuring valuable leads go to those most likely to convert them.
Limitations: May create morale issues if perceived as unfair by newer or developing team members.
Hybrid Models
Many organizations implement combinations of these approaches, creating weighted algorithms that consider multiple factors when assigning leads.
Best for: Complex sales organizations with diverse teams and lead types.
Limitations: Requires sophisticated systems and careful calibration to avoid unintended consequences.
Step 4: Select the Right Technology Solution
With your requirements and preferred distribution model defined, you can evaluate technology solutions to power your system.
Types of Lead Distribution Technology
CRM-Based Solutions: Many modern CRMs include built-in distribution capabilities or offer apps/integrations that add this functionality.
Dedicated Lead Distribution Software: Specialized platforms focus exclusively on lead routing and management, often with more sophisticated options.
Custom-Built Systems: Some organizations with unique requirements develop proprietary solutions tailored to their specific processes.
Key Features to Evaluate
When assessing potential solutions, consider:
Rule Configuration Flexibility: How easily can you set up and modify your distribution rules?
Integration Capabilities: Does the system connect seamlessly with your existing tech stack?
Scalability: Can it handle your projected growth in lead volume and team size?
Analytics and Reporting: What insights does it provide about distribution effectiveness?
Automation Features: How much of the process can be automated to reduce manual intervention?
User Experience: Is the interface intuitive for both administrators and sales representatives?
Mobile Functionality: Can representatives receive and claim leads on mobile devices?
Support and Training: What resources are available to help your team adopt the system?
Implementation Considerations
Before finalizing your selection, evaluate:
- Time required for implementation
- Resources needed for setup and configuration
- Training requirements for different user groups
- Data migration needs
- Testing protocols before full deployment
Step 5: Design Your Lead Distribution Rules
The heart of your distribution system lies in the rules that govern how leads are assigned. These rules should reflect your chosen model while accounting for your organization's unique characteristics.
Define Lead Qualification Criteria
Before distribution, establish clear parameters for lead quality:
- What constitutes a marketing qualified lead (MQL)?
- What additional information is required before sales assignment?
- Are there minimum threshold scores or actions required?
- How will lead scoring be incorporated into the distribution process?
Establish Lead Routing Logic
Create detailed decision trees that determine how leads flow through your system:
- Primary routing factors (geography, industry, product interest, etc.)
- Secondary considerations if primary matches aren't available
- Escalation paths for high-priority leads
- Handling of after-hours inquiries
- Protocols for redistributing unaccepted or stale leads
Set Time-Based Rules
Implement timing guidelines that ensure prompt handling:
- Maximum wait time before lead assignment
- Response time expectations after assignment
- Follow-up frequency requirements
- Aging thresholds for inactive leads
- Re-engagement protocols for dormant leads
Create Exception Handling Procedures
Determine how your system will manage special cases:
- VIP or strategic account inquiries
- Existing customer referrals
- Leads from specific high-value campaigns
- Requests for specific sales representatives
- Overflow handling during peak periods
Step 6: Implement and Test Your System
With your technology and rules defined, you're ready to implement your lead distribution system.
Phased Implementation Approach
Consider a gradual rollout:
- Begin with a pilot team or limited lead sources
- Test all components in a controlled environment
- Gather feedback and make necessary adjustments
- Gradually expand to additional teams or lead types
- Monitor closely during expansion phases
Comprehensive Testing Protocol
Test various scenarios to ensure your system handles them appropriately:
- High-volume periods
- After-hours inquiries
- Multiple simultaneous leads
- Representatives being unavailable or at capacity
- Integration points with other systems
- Mobile functionality
- Reporting accuracy
Training and Documentation
Prepare thorough materials for all users:
- System administrators
- Sales managers
- Individual representatives
- Marketing team members
- Operations personnel
Ensure training covers not just how to use the system but why specific processes and rules exist.
Step 7: Monitor, Measure, and Optimize
A lead distribution system is never truly "finished." Ongoing monitoring and refinement are essential for maintaining and improving its effectiveness.
Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Track metrics that measure system effectiveness:
- Lead response time
- Time to first meaningful contact
- Lead acceptance rate by representatives
- Conversion rates by lead source and representative
- Distribution equity across team members
- Exception rates and manual intervention frequency
Regular Review Cadence
Implement structured evaluation periods:
- Daily operational checks for technical issues
- Weekly team reviews of distribution patterns
- Monthly analysis of conversion metrics
- Quarterly strategic assessments of overall system performance
Continuous Improvement Process
Create mechanisms for ongoing refinement:
- Regular stakeholder feedback sessions
- A/B testing of distribution rule variations
- Analysis of top performer behaviors
- Adaptation to changing market conditions
- Integration of new data sources or technologies
Common Challenges and Solutions in Lead Distribution
Even well-designed lead distribution systems can face challenges. Being prepared to address these issues will help maintain system effectiveness.
Challenge: Sales Representative Resistance
Symptoms:
- Representatives bypassing the system to select preferred leads
- Complaints about lead quality or distribution fairness
- Low adoption rates of new processes
Solutions:
- Involve representatives in system design from the beginning
- Implement transparent distribution algorithms that are perceived as fair
- Provide clear visibility into how leads are assigned
- Create feedback mechanisms for flagging lead quality issues
- Demonstrate system value through improved conversion metrics
Challenge: Integration Issues
Symptoms:
- Data inconsistencies between systems
- Delays in lead transfer between platforms
- Missing information in lead records
Solutions:
- Implement robust API connections between systems
- Create data validation rules to ensure completeness
- Establish error notification protocols for failed transfers
- Develop fallback procedures for when integrations experience issues
- Regular audits of data flow between systems
Challenge: Scaling Problems
Symptoms:
- System slowdowns during high-volume periods
- Increasing manual interventions needed
- Growing exception cases not covered by rules
Solutions:
- Design with scalability in mind from the beginning
- Stress test systems with projected peak volumes
- Implement queue management for high-volume periods
- Create dynamic rules that adapt to changing conditions
- Regular review and updating of distribution logic
Challenge: Measuring True Impact
Symptoms:
- Difficulty attributing performance improvements to the distribution system
- Conflicting metrics showing different results
- Uncertainty about ROI from the implementation
Solutions:
- Establish baseline metrics before implementation
- Use control groups where possible during rollout phases
- Track multiple layers of metrics (activity, efficiency, outcomes)
- Correlate distribution patterns with ultimate sales results
- Gather qualitative feedback alongside quantitative measures
Advanced Strategies for Lead Distribution Excellence
Once your basic lead distribution system is functioning effectively, consider these advanced approaches to further enhance performance.
Predictive Lead Scoring Integration
Move beyond basic lead qualification by implementing machine learning algorithms that dynamically score leads based on:
- Behavioral patterns that correlate with conversion
- Company firmographic data
- Individual interaction history
- Market timing signals
- Competitive positioning factors
These scores can then be incorporated into your distribution rules, ensuring the most promising leads receive priority attention.
AI-Powered Lead-to-Rep Matching
Advanced systems can analyze historical performance data to identify patterns in which representatives excel with specific lead types. These systems continuously learn and adjust, creating increasingly precise matches over time.
Consider factors such as:
- Communication style preferences
- Industry knowledge alignment
- Product expertise relevance
- Past success with similar company profiles
- Geographic or cultural affinities
Real-Time Optimization
Implement dynamic distribution systems that adjust in real-time based on:
- Current conversion performance metrics
- Representative availability and capacity
- Time-sensitive opportunity windows
- Changing lead characteristics
- Market condition shifts
These systems can rebalance distribution rules without manual intervention, ensuring optimal performance even as conditions change.
Closed-Loop Analytics
Create feedback mechanisms that track the entire lead journey from initial touch to closed business, providing insights into:
- Which distribution patterns yield the highest conversion rates
- How different lead sources perform when matched with various representatives
- The true lifetime value of leads from different channels
- Optimal follow-up sequences for different lead types
- Early indicators of high-potential opportunities
This information can then be fed back into your distribution rules, creating a continuously improving system.
Conclusion: The Future of Lead Distribution Systems
As businesses continue to evolve in an increasingly digital landscape, lead distribution systems will play an even more critical role in sales success. Organizations that implement sophisticated, data-driven distribution processes gain a significant competitive advantage through improved efficiency, higher conversion rates, and better customer experiences.
The most effective lead distribution systems are not static implementations but dynamic frameworks that continuously adapt based on performance data and changing market conditions. By following the steps outlined in this guide and remaining committed to ongoing optimization, you can create a lead distribution system that not only meets your current needs but evolves alongside your business.
Remember that technology is only one component of successful lead management. Equally important are clear processes, well-trained team members, and a culture that values prompt, professional follow-up with every potential customer. When these elements align within a thoughtfully designed distribution framework, the result is a powerful sales engine that maximizes the value of every lead that enters your pipeline.
By investing in creating and refining your lead distribution system, you're not just implementing a process—you're building a foundation for sustainable sales growth and customer acquisition excellence.
Add to Conversation
Routera Team
Content Team